| Visual Basic (Declaration) | |
|---|---|
Public Property SourceFields As CsvLayer.FieldCollection | |
| C# | |
|---|---|
public CsvLayer.FieldCollection SourceFields {get; set;} | |
If it is not desired to convert all of the fields of information in the CSV records into a CsvLayer use the SourceFields Property to set exactly which fields will become attributes in the CsvLayer. If the SourceFields Property is not specified then all fields of information in the CSV file will be used to populate the attributes in the CsvLayer. To restrict which fields are generated in the CsvLayer using the SourceFields Property, create a new the CsvLayer.FieldCollection object and add the specific Field objects with the minimum Properties of Field.FieldName and Field.Type being set. The Field.FieldName should match the header name contained inside the CSV file. If Field.Type is not provided field type will default to string.
How to use:
Click the Button to add a CsvLayer to the Map. The ID of the layer and its attribute information will displayed in the TextBox.
The XAML code in this example is used in conjunction with the code-behind (C# or VB.NET) to demonstrate the functionality.
The following is an example of the ASCII contents for the file named US_Cities_Top_3_ManyFields.csv:
ID,Y,X,City,Useless,Population,Clueless,What,MyDate
1,40.714,-74.006,NYC,XXX,8244910,QQQ,GGG,12/1/2012
2,34.0522,-118.244,LA,YYY,3819702,AAA,TTT,12/2/2012
3,41.878,-87.636,Chicago,ZZZ,2708120,ZZZ,UUU,12/3/2012
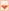
The following screen shot corresponds to the code example in this page.

| XAML |  Copy Code Copy Code |
|---|---|
<Grid x:Name="LayoutRoot" > <!-- Add a Map Control to the application. Set the Extent to North America. --> <esri:Map x:Name="Map1" HorizontalAlignment="Left" VerticalAlignment="Top" Margin="0,212,0,0" Height="376" Width="415" Extent="-15219969,2609636,-6232883,6485365"> <!-- Add a backdrop ArcGISTiledMapServiceLayer. --> <esri:ArcGISTiledMapServiceLayer ID="World_Topo_Map" Url="http://services.arcgisonline.com/arcgis/rest/services/world_topo_map/MapServer" /> </esri:Map> <!-- Add a Button that will allow the user to add a CsvLayer via code-behind. --> <Button Name="Button1" Height="23" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="0,183,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="706" Content="Add a CsvLayer (via code-behind) for the specified Url." Click="Button1_Click" /> <!-- TextBox to display attribute information about about the CsvLayer added to the Map. --> <TextBox Height="376" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="421,212,0,0" Name="TextBox1" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="285" /> <!-- Provide the instructions on how to use the sample code. --> <TextBlock Height="174" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Name="TextBlock1" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="788" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="Click the Button to add a CsvLayer to the Map. The ID of the layer and its attribute information will displayed in the TextBox." /> </Grid> | |
| C# |  Copy Code Copy Code |
|---|---|
private void Button1_Click(object sender, System.Windows.RoutedEventArgs e) { // This function executes as a result of the user clicking the Button. It adds a CsvLayer using code-behind. // Create a CsvLayer. ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Toolkit.DataSources.CsvLayer myCsvLayer = new ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Toolkit.DataSources.CsvLayer(); // Set the Url of the CsvLayer to a public service. // NOTE: you need to adjust the Url to a .csv file served up on you test web server. myCsvLayer.Url = "http://www.yourserver.com/CSV_Files/US_Cities_Top_3_ManyFields.csv"; // Set the ID of the CsvLayer. myCsvLayer.ID = "US_Cities_Top_3_ManyFields"; // Create a FieldCollection object to define what Fields from the CSV file will be imported into the CsvLayer. ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Toolkit.DataSources.CsvLayer.FieldCollection theSourceFields = null; theSourceFields = new ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Toolkit.DataSources.CsvLayer.FieldCollection(); // Define the Field objects that will be read in from the CSV file. // NOTE: not all of the attribute fields that are in the CSV file will be converted to Fields in the CsvLayer. ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field theIDfield = new ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field(); theIDfield.FieldName = "ID"; theIDfield.Type = ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field.FieldType.OID; ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field theXfield = new ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field(); theXfield.FieldName = "X"; theXfield.Type = ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field.FieldType.Double; ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field theYfield = new ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field(); theYfield.FieldName = "Y"; theYfield.Type = ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field.FieldType.Double; ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field theCity = new ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field(); theCity.FieldName = "City"; theCity.Type = ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field.FieldType.String; ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field thePopulation = new ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field(); thePopulation.FieldName = "Population"; thePopulation.Type = ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field.FieldType.Integer; ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field theMyDate = new ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field(); theMyDate.FieldName = "MyDate"; theMyDate.Type = ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field.FieldType.Date; // Add the defined Fields into the FieldCollection object. theSourceFields.Add(theIDfield); theSourceFields.Add(theXfield); theSourceFields.Add(theYfield); theSourceFields.Add(theCity); theSourceFields.Add(thePopulation); theSourceFields.Add(theMyDate); // Set the custom FieldCollection to the CsvLayer.SourceFields Property. myCsvLayer.SourceFields = theSourceFields; // Create a SimpleMarkerSymbol (a red traingle) for the CsvLayer that will be added. ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Symbols.SimpleMarkerSymbol theSimpleMarkerSymbol = new ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Symbols.SimpleMarkerSymbol(); theSimpleMarkerSymbol.Color = new System.Windows.Media.SolidColorBrush(System.Windows.Media.Colors.Red); theSimpleMarkerSymbol.Size = 18; theSimpleMarkerSymbol.Style = ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Symbols.SimpleMarkerSymbol.SimpleMarkerStyle.Triangle; // Define a SimpleRenderer and set the Symbol to the SimpleMarkerSymbol. ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.SimpleRenderer theSimpleRenderer = new ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.SimpleRenderer(); theSimpleRenderer.Symbol = theSimpleMarkerSymbol; // Define the Renderer for the CsvLayer. myCsvLayer.Renderer = theSimpleRenderer; // Wire-up the Initialized Event of the CsvLayer. myCsvLayer.Initialized += CsvLayer_Initialized; // Add the CsvLayer to the Map. Map1.Layers.Add(myCsvLayer); } private void CsvLayer_Initialized(object sender, EventArgs e) { // This function will execute as a result of the CsvLayer that was defined in code-behind being Initialized. // Get the CsvLayer. ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Toolkit.DataSources.CsvLayer myCsvLayer = (ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Toolkit.DataSources.CsvLayer)sender; // Get the ID of the CsvLayer. string myID = myCsvLayer.ID; // Create a StringBuilder object to hold information about the CsvLayer and add some useful information to it. System.Text.StringBuilder myStringBuilder = new System.Text.StringBuilder(); myStringBuilder.Append("The CsvLayer and it's ID is: " + Environment.NewLine); myStringBuilder.Append(myID + Environment.NewLine); myStringBuilder.Append("====================================" + Environment.NewLine); // Get the GraphicCollection from the CsvLayer. ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.GraphicCollection theGraphicCollection = myCsvLayer.Graphics; if (theGraphicCollection != null) { // Loop through each Graphic. foreach (ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Graphic oneGraphic in theGraphicCollection) { // Get the Attribute Keys. System.Collections.Generic.ICollection<string> theFieldNameKeys = oneGraphic.Attributes.Keys; // Loop through each Attribute. foreach (var oneKey in theFieldNameKeys) { // Get the value of the Attribute Field. string theValue = oneGraphic.Attributes[oneKey].ToString(); // Get the Type of the Attribute Field. string oneFieldType = oneGraphic.Attributes[oneKey].GetType().ToString(); // Add the Attribute Field name, OS data type, and Attribute value to the StringBuilder object. myStringBuilder.Append(oneKey.ToString() + "(" + oneFieldType + "): " + theValue + Environment.NewLine); } myStringBuilder.Append(Environment.NewLine); } } // Display the results of the StringBuilder text to the user. TextBox1.Text = myStringBuilder.ToString(); } | |
| VB.NET |  Copy Code Copy Code |
|---|---|
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As System.Object, e As System.Windows.RoutedEventArgs) ' This function executes as a result of the user clicking the Button. It adds a CsvLayer using code-behind. ' Create a CsvLayer. Dim myCsvLayer As ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Toolkit.DataSources.CsvLayer = New ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Toolkit.DataSources.CsvLayer ' Set the Url of the CsvLayer to a public service. ' NOTE: you need to adjust the Url to a .csv file served up on you test web server. myCsvLayer.Url = "http://www.yourserver.com/CSV_Files/US_Cities_Top_3_ManyFields.csv" ' Set the ID of the CsvLayer. myCsvLayer.ID = "US_Cities_Top_3_ManyFields" ' Create a FieldCollection object to define what Fields from the CSV file will be imported into the CsvLayer. Dim theSourceFields As ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Toolkit.DataSources.CsvLayer.FieldCollection theSourceFields = New ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Toolkit.DataSources.CsvLayer.FieldCollection ' Define the Field objects that will be read in from the CSV file. ' NOTE: not all of the attribute fields that are in the CSV file will be converted to Fields in the CsvLayer. Dim theIDfield As ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field = New ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field theIDfield.FieldName = "ID" theIDfield.Type = ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field.FieldType.OID Dim theXfield As ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field = New ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field theXfield.FieldName = "X" theXfield.Type = ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field.FieldType.Double Dim theYfield As ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field = New ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field theYfield.FieldName = "Y" theYfield.Type = ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field.FieldType.Double Dim theCity As ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field = New ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field theCity.FieldName = "City" theCity.Type = ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field.FieldType.String Dim thePopulation As ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field = New ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field thePopulation.FieldName = "Population" thePopulation.Type = ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field.FieldType.Integer Dim theMyDate As ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field = New ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field theMyDate.FieldName = "MyDate" theMyDate.Type = ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Field.FieldType.Date ' Add the defined Fields into the FieldCollection object. theSourceFields.Add(theIDfield) theSourceFields.Add(theXfield) theSourceFields.Add(theYfield) theSourceFields.Add(theCity) theSourceFields.Add(thePopulation) theSourceFields.Add(theMyDate) ' Set the custom FieldCollection to the CsvLayer.SourceFields Property. myCsvLayer.SourceFields = theSourceFields ' Create a SimpleMarkerSymbol (a red traingle) for the CsvLayer that will be added. Dim theSimpleMarkerSymbol As ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Symbols.SimpleMarkerSymbol = New ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Symbols.SimpleMarkerSymbol theSimpleMarkerSymbol.Color = New System.Windows.Media.SolidColorBrush(System.Windows.Media.Colors.Red) theSimpleMarkerSymbol.Size = 18 theSimpleMarkerSymbol.Style = ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Symbols.SimpleMarkerSymbol.SimpleMarkerStyle.Triangle ' Define a SimpleRenderer and set the Symbol to the SimpleMarkerSymbol. Dim theSimpleRenderer As ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.SimpleRenderer = New ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.SimpleRenderer theSimpleRenderer.Symbol = theSimpleMarkerSymbol ' Define the Renderer for the CsvLayer. myCsvLayer.Renderer = theSimpleRenderer ' Wire-up the Initialized Event of the CsvLayer. AddHandler myCsvLayer.Initialized, AddressOf CsvLayer_Initialized ' Add the CsvLayer to the Map. Map1.Layers.Add(myCsvLayer) End Sub Private Sub CsvLayer_Initialized(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) ' This function will execute as a result of the CsvLayer that was defined in code-behind being Initialized. ' Get the CsvLayer. Dim myCsvLayer As ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Toolkit.DataSources.CsvLayer = CType(sender, ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Toolkit.DataSources.CsvLayer) ' Get the ID of the CsvLayer. Dim myID As String = myCsvLayer.ID ' Create a StringBuilder object to hold information about the CsvLayer and add some useful information to it. Dim myStringBuilder As New Text.StringBuilder myStringBuilder.Append("The CsvLayer and it's ID is: " + vbCrLf) myStringBuilder.Append(myID + vbCrLf) myStringBuilder.Append("====================================" + vbCrLf) ' Get the GraphicCollection from the CsvLayer. Dim theGraphicCollection As ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.GraphicCollection = myCsvLayer.Graphics If theGraphicCollection IsNot Nothing Then ' Loop through each Graphic. For Each oneGraphic As ESRI.ArcGIS.Client.Graphic In theGraphicCollection ' Get the Attribute Keys. Dim theFieldNameKeys As System.Collections.Generic.ICollection(Of String) = oneGraphic.Attributes.Keys ' Loop through each Attribute. For Each oneKey In theFieldNameKeys ' Get the value of the Attribute Field. Dim theValue As String = oneGraphic.Attributes(oneKey) ' Get the Type of the Attribute Field. Dim oneFieldType As String = oneGraphic.Attributes(oneKey).GetType.ToString ' Add the Attribute Field name, OS data type, and Attribute value to the StringBuilder object. myStringBuilder.Append(oneKey.ToString + "(" + oneFieldType + "): " + theValue + vbCrLf) Next myStringBuilder.Append(vbCrLf) Next End If ' Display the results of the StringBuilder text to the user. TextBox1.Text = myStringBuilder.ToString End Sub | |
Target Platforms: Windows XP Professional, Windows Server 2003 family, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 family, Windows 7, Windows 8