AIXM
The Aeronautical Information Exchange Model (AIXM) is designed to be the global standard for transfer of aeronautical data in digital format. It was developed by the European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation (EUROCONTROL) and the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), with participation from other industry stakeholders.
AIXM is based on:
- ICAO Annex 15
- ARINC, RTCA and other industry specifications
- Aeronautical information publications
- Other standards and best practices
- Other aspects of the aeronautical domain that have not been subjected to formal requirements
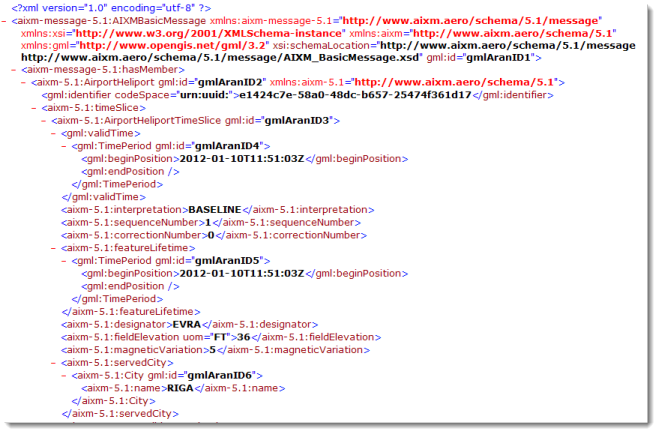
The current version of AIXM 5.1 is built upon the following standards and specifications: UML, GML 3.2, and ISO standards (including metadata). A portion of a sample AIXM message is shown below.
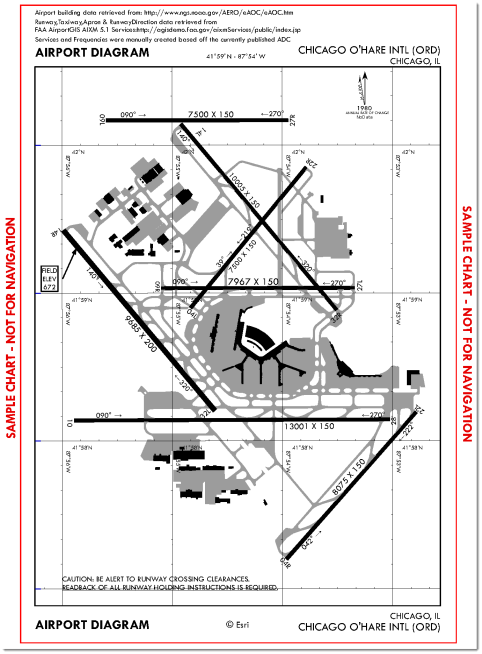
At the center of the ArcGIS for Aviation: Charting 10.1 release is an AIXM 5.1-compliant data model. From this data model, aeronautical charts of all types (Enroute, Planning, IAP's, etc.) can be created and maintained. The figure below illustrates an Airport Diagram chart created from AIXM 5.1 sample data that was loaded into a geodatabase and produced using ArcGIS for Aviation: Charting.
As mentioned above, AIXM is a standard by which aeronautical information can be transferred from one organization/agency to another. ArcGIS for Aviation: Charting can be used to both import and export AIXM data through the use of data loaders created using the ArcGIS Data Interoperability extension. Currently, the solution allows for import and export of AIXM 4.5 data (e.g. EAD data feeds). As AIXM 5.1 data becomes more prevalent capabilities for ingesting and exporting this will be added to ArcGIS for Aviation: Charting.
eTOD
Terrain and obstructions (buildings, power lines, etc.) pose risks to the safe departure, cruise, and arrival of aircraft. In order to continuously evaluate obstructions and to ensure safe operations, ICAO Annex 15 was adopted and established for electronic terrain and obstacle database (eTOD) requirements.
Four geographical areas are defined and evaluated against obstructions and terrain.
|
Area 1 |
State Level |
|
Area 2 |
Terminal Control Area |
|
Area 3 |
Aerodrome Area |
|
Area 4 |
CAT II/III Operation Area |
The AIS data model in ArcGIS for Aviation: Charting assists in complying with the ICAO Annex requirements by providing the feature classes necessary to collect, manage, and store obstruction data. You can identify obstacles as points, lines, or polygons and relate those specific obstacles to a defined area through a relationship class in the geodatabase. The obstacle feature classes have been modeled according to the feature catalog in ICAO Doc 9881. eTOD datasets can then be exported as an AIXM 4.5 file to provide to your end users.
The eTOD standard is further supported by two geoprocessing tools which automate the creation of obstacle identification surfaces (OIS) according to ICAO Annexes 14 and 15. Once these surfaces are created for a runway, obstacles and terrain can be visualized and analyzed in 2D or 3D to ensure safe operations by arriving and departing aircraft at the airport. The figure below illustrates terrain data which penetrates an Annex 14 OIS.

ICAO
ICAO Annex 4, Aeronautical Charts, outlines the standards and recommended practices applicable to types of aeronautical charts defined in the Annex. ArcGIS for Aviation: Charting provides chart templates, fonts, and style files for the following ICAO charts:
- World Aeronautical Chart - 1:1,000,000
- Aeronautical Chart - 1:500,000
- Enroute Chart
- Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID)
- Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR)
- Instrument Approach Chart
- Visual Approach Chart
- Aerodrome/Heliport Chart
- ATC Surveillance Minimum Altitude Chart
These templates and symbols can be used out-of-the-box or configured to meet the specific charting requirements of your organization. A sample gallery of charts generated using ArcGIS for Aviation: Charting can be accessed here.
OGC
As part of the ArcGIS system, you can take full advantage of the geospatial and location standards developed by the OGC. Standards relevant to aviation such as GML, WFS, and WCS have been developed by OGC and allow for the sharing and interoperability of geospatial data across various software platforms.
The ArcGIS for Aviation team is committed to supporting the development of standards in an industry that is increasingly dependent on them.
ISO
ArcGIS for Aviation is developed in accordance with an ISO 9001:2008 certified process. The Quality Management System in place ensures a standardized and approved methodology is followed during the software development cycle. Regularly scheduled internal and external audits are conducted to certify compliance with documented processes.
